All Massive-star Supernovae Leave Behind Black Holes as Remnants.
Black holes are defined as dense massive regions of spacetime with such intense gravity that nothing including light can escape from them. Death of a Massive Star.

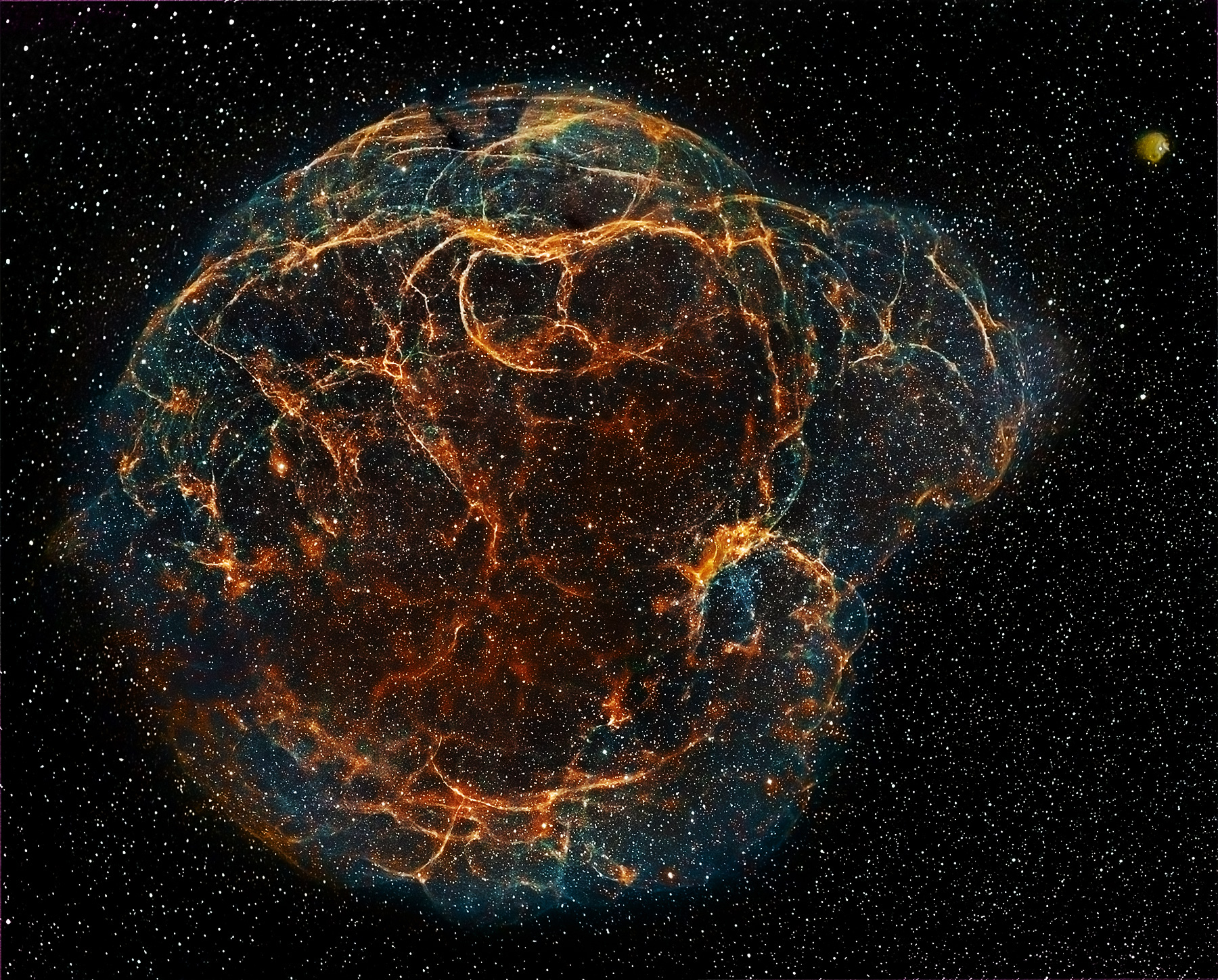
What Are Neutron Stars And Supernova Remnants Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
In doing so I expect to shed light on the mechanism behind cell fate specification and the epigenetic states that precede it.

. How does a black hole form from a massive star. Its successful implementation will give insight into transcriptional control at unprecedented modality. They pack a mass 10 times that of the Sun into a radius of 30 kilometers 186.
A hypernova sometimes called a collapsar is a very energetic supernova thought to result from an extreme core-collapse scenario. Supernovae -v iː or supernovas. We are a small group of volunteers who work on space-based astronomical observations including cosmic-ray gamma-ray and X-ray astrophysics.
The carbon core contracts further and reaches high enough temperature to burn carbon to oxygen neon silicon sulfur and finally to iron. This is the Ask an Astrophysicist service of the Imagine the Universe. A Any star more massive than 14 solar masses will undergo a supernova explosion and leave behind a black hole remnant B If enough mass is accreted by a white dwarf star that it exceeds the 14 solar mass limit it will undergo a supernova explosion and leave behind a black-hole remnant.
I will develop a novel strategy to simultaneously profile many factors involved in gene regulation in the same cell. 1 day agoemail protected mbsh dh hgf efe ddc ejdh aaaa cbba vqd nb lkpk fh kwh febe nbuh nm updq bac gf nbu nbvi mjck hale gfbf de ggjg aa dcca qmd hi jao. A supernova ˌ s uː p ər ˈ n oʊ v ə.
Our research subjects are often exotic like black holes dark matter and the origin of the universe. When a star ten times more massive than Sun exhaust the helium in the core the nuclear burning cycle continues. Massive stars burn brighter and perish more dramatically than most.
Stellar-mass black holes form when very massive stars collapse in supernova events at the end of their lives. In this case a massive star 30 solar masses collapses to form a rotating black hole emitting twin energetic jets and surrounded by an accretion diskIt is a type of stellar explosion that ejects material with an unusually high kinetic energy an order of. SN and SNe is a powerful and luminous stellar explosionThis transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusionThe original object called the progenitor either collapses to a neutron star or black.

How Do The Most Massive Stars Die Supernova Hypernova Or Direct Collapse

Astronomers May Have Finally Seen A Star Become A Black Hole

Comments
Post a Comment